You must have noticed that this article is about modular programming. A concept that many of us as programmers may not know much about. So if you want to get information about software modules and understand how to do modular coding, stay tuned to the “What is modular programming” article on W3camps.
If you read this article, you are probably a programmer or at least interested in programming. Are you a senior or junior programmer? Being a junior is not a problem because all senior programmers were once juniors. However, the problem is to stay an amateur. In the “What is modular programming” article, I want to introduce one of the ways of becoming a professional programmer.
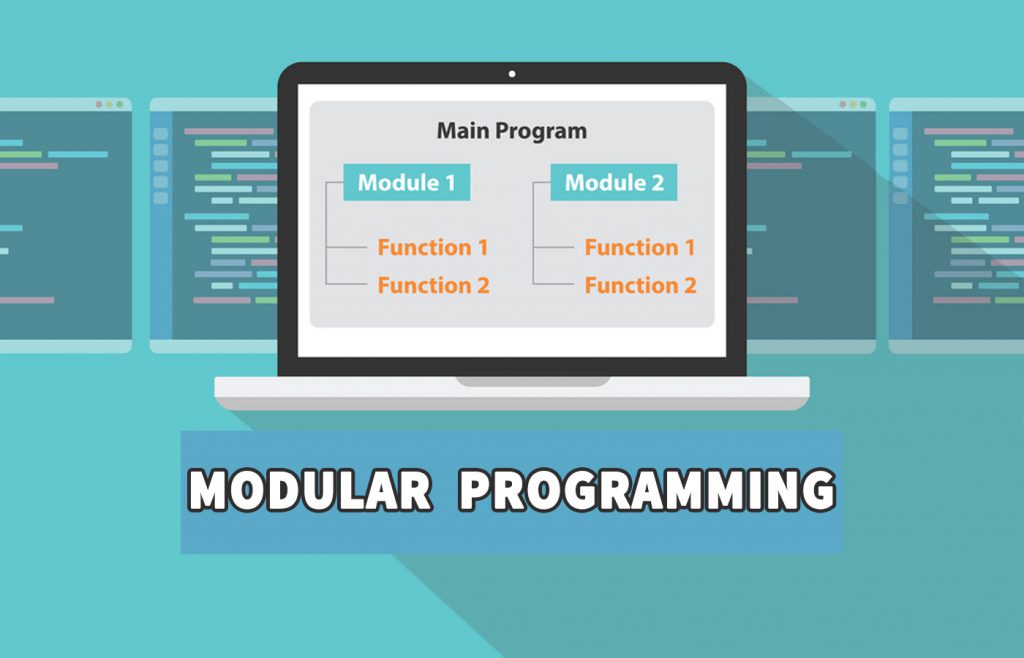
One of the factors that makes you professional is knowing modular programming. Let me give you a definition of modular programming. Modular programming is a software design technique in which a program is divided into independent and interchangeable modules. Each of these modules contains all the necessary code to be able to run a part of the main program. This modular programming definition may sound a bit vague to you, so let’s explain it more to be understood.
Modular programming meaning

To make modular programming meaning clear, we explain the concept of software modules in detail. A module is a component or part of a program that contains several related functions. Usually, the set of functions inside a module implements a specific function. Some modules perform a process on the data. In this type of module, part of the program as a client requests a service from the module and the module responds to that request. Each module consists of two parts:
- The implementation
- The interface
One of the primary objectives of employing modules is to facilitate the identification of essential components while concealing superfluous ones. This concealment of unnecessary intricacies is termed abstraction, a concept widely employed in various device designs. For instance, when operating a car, intricate knowledge of the engine’s internal workings isn’t requisite; familiarity with the engine usage interface suffices, including understanding the operation of the clutch, brake, and accelerator pedals.
One of the main reasons for using the module is to be able to identify the necessary parts and hide the unnecessary ones. Hiding unnecessary details is called abstraction. This concept is used in many device designs. For example, when driving a car, we do not necessarily need to know how the engine and other components work, but it is enough to have the engine usage interface (including clutch, brake, and accelerator pedals) and Know how to use this interface.
In programming, Abstraction is a very valuable concept that is well-supported in object-oriented languages (such as Java and C++) and in basic modular languages.
It allows programmers to focus on essential functionalities while obscuring complex implementation details, thereby enhancing code readability and maintainability. By encapsulating functionalities within modules, developers can foster code reusability, scalability, and modularity, facilitating collaborative development efforts and streamlining software maintenance processes. Additionally, abstraction promotes a clear separation of concerns, enabling developers to isolate and address specific functionalities independently, fostering code cohesion and minimizing potential dependencies.
Advantages of modular programming
When you get involved in a real programming job; The situation will be very different with coding for learning. Because in this situation, you will be dealing with a substantial code and different dimensions, which is beyond the ability of one person to do. The group writes such a code, and its debugging capabilities must be predicted and implemented in advance.
Also, different members should be able to combine their code and produce the final software. Of course, this software must be maintained and upgraded in the future. These are just some of the benefits of this programming style. In the following, we will evaluate some of them in more detail.
Code readability
Modular programming fosters organization by allowing programmers to focus on specific tasks within a larger project. Each programmer writes code for a particular module, making it easier for others to understand and continue the work. This approach minimizes ambiguity in code comprehension, enhancing overall readability and maintainability.
Straightforward debugging
Modular programming simplifies the debugging process by providing clear boundaries between different modules. When an error occurs, programmers can easily locate the source within the relevant module, facilitating quicker fixes. In contrast, debugging non-modular code often entails searching through extensive lines of code, which is less efficient and more time-consuming.
Code maintenance
When an organization writes a program, it is definitely thinking about maintaining and updating it in the future because new needs are defined for customers over time and updates are required. Modular programs are inherently designed with future maintenance and updates in mind. As new requirements emerge over time, it’s easier to identify and modify specific modules without necessitating extensive changes to the entire codebase. This modular approach streamlines maintenance efforts compared to non-modular approaches, where even minor updates may require significant code revisions.
Team coding
Modular programming facilitates collaborative development by enabling tasks to be divided among team members based on their expertise. Project managers can assign individuals to work on specific modules, allowing for parallel development. Experienced team members can then integrate these modules to produce the final software, leveraging the collective contributions of the team.
Terms of use of modular programming
This section refers to the conditions in which the modular coding style must be used. A situation in which we encounter many problems without using this method.
Market competition
A programmer who has to write all the code for each new project cannot compete in the market because they have to code from scratch, and as a result, the project’s execution time is longer, and it lags behind the competitors.
You may think that each project is different and needs to be coded separately. Yes, that is right, but there are many small parts in various projects that are similar. In other words, once you have written the code, you can easily use it in the upcoming projects with a bit of change.
In the implementation of large and complex projects, if the proper programming style is not used, the maintenance and debugging of the code becomes very harsh, costs increase, and the possibility of the project’s success is minimized.
Developments within organizations
Employees’ job positions change in an organization, and even if they are fixed, their memory recalls a limited period of time, therefore programs need to be written and documented correctly in order to upgrade and update systems. Otherwise, it will be difficult to understand and change them.
Also, It is crucial to break down large projects into smaller components and implement each section individually or as an independent team. It is possible to create software components and libraries that could easily be modified and used in other projects using a modular programming style. A good program can be understood and changed at any time not just by the original designer, but by others.
Implementation method
After understanding the definition of modular programming and the context of this coding method, it is time for hands on practice. The programming language must be able to reuse the code and create flexible libraries so that the programmer can use libraries that have been tested, debugged, and verified in future projects.
Usually, the smallest component that performs essential tasks in a program is called a function. The function has a specific job. It receives data from one part of the program, processes it, and delivers it to another part. As we have mentioned, these tasks are repeated in various programs and projects. So we can define and write them once in a program and Then use them many times.
Modular programming in C language
Now we want to write the initial definition of a sample function. To avoid complexity, we use the C language. Using source and header files, we could implement modular programming in the C language. First, we implement a function in a file named “sample.c” as follows:
#include "sample.h"
char sample_var;
char sample_function(void)
{
//function body
}Then we enter the required definitions in a file called “sample.h“, which is the file’s header so that it is easier to identify the sources of our definitions as the modules increase.
extern sample_var;
extern sample_function();After defining the “sample_function” in the code, we can use it wherever it is in the range of this function. Therefore, we use it in the main function.
#include "sample.h"
int main(void)
{
char var;
var = sample_function();
//function body
}So far, we have built a straightforward module and used it in the main function. We can now transfer it to other programs and use it through the library or other methods.
Note: the person using this module does not necessarily need to be aware of its content and functionality. It is enough to know what the arguments are to be given to the module parameters and what operations are performed on them in the end. In fact, the programmer knows what output to expect from the module.
Modular programming in Python
We could use modular programming in Python in a similar way. If you are not familiar with Python, you can study the “Why should I learn python” article.
A module is typically any Python file that contains classes and functions. An appropriate example of a module you might have used before is the time module. Also, we can create and import our own modules. Here is the “my_module.py” Python code:
def function1(item):
return item * 4
def function2(item):
return item + 26We could use the import keyword in Python to import built-in modules or that we have created. In the following, we import “my_module.py” in “main.py” file:
import my_module
value = my_module.function1(5)
# this will call the function1 from my_module
print(value)
# this prints 20Note: To import our own modules they must be located in the same directory as the project’s file.
To avoid the use of “my_module” we can import specific functions from our modules using a combination of keywords “import” and “from”:
from my_module import function2
value = function2(10)
# now we can just use function2 like a regular function
print(value)
# this prints 36Final words
We almost discussed everything you need to about modular programming. It doesn’t matter if you are a web developer, artificial intelligence developer, etc. In any field you work in, use a modular coding approach in order to use the codes for a long time.
If the article is not understandable to you, do not worry at all, because you need to read and review it more times. Do not forget to introduce us to your friends, our content may be useful for them.

I am extremely inspired together with your writing abilities and
also with the layout on your blog. Is that this a paid theme or did you
modify it your self? Anyway keep up the excellent quality writing, it is
rare to see a nice weblog like this one nowadays.